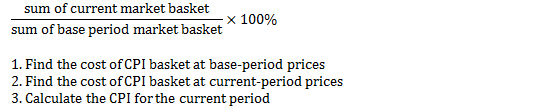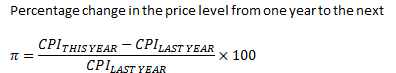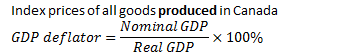Ch 21 - Unemployment, Inflation
Monday, January 23, 2012
11:42 PM
- Redistributes income and wealth
- Diverts resources from production
- Select CPI basket
- Conduct price survey
- Use prices and the basket to calculate CPI
- Distorts private contracts
- Increase government outlays
- Inaccurate estimates of real earnings
|
Working-age population |
The total number of people age 15 years and older |
|
Labour force |
The sum of employed and the unemployed |
|
Unemployment rate |
|
|
Labour force participation rate |
|
|
Employment-to-population ratio |
|
|
Marginally attached worker |
Person who currently is neither working nor looking for work but want job when available |
|
Discouraged worker |
Marginally attached worker who has stopped looking for a job |
|
Frictional unemployment |
From normal labour turnover |
|
Structural unemployment |
From changes in technology or international competition |
|
Cyclical unemployment |
From business cycle though and peak. |
|
Natural unemployment |
Only frictional and structural |
|
Full employment |
Unemployment rate = natural unemployment rate (no cyclical) |
![]() Price
Level & Inflation
Price
Level & Inflation
|
Price level |
The average level of prices and the value of money |
|
Inflation rate |
The annual percentage change in the price level |
Inflation is a problem because
|
Hyperinflation |
An rapidly increasing inflation rate |
CPI
|
Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
Measures the average of the prices paid by urban consumers for a "fixed" basket of goods/services |
|
Reference base period |
CPI = 100 for the first period |
|
Calculating the CPI |
|
Construct the CPI
|
Inflation rate |
|
Biased CPI
|
New goods |
New goods that replace old goods in basket (iPod vs. CD player) |
|
Quality change |
Quality improvements that lead to price changes are wrongly considered as inflation |
|
Commodity substitution |
Does not consider consumer's substitutions for goods in basket |
|
Outlet substitution |
Outlets undervalue certain goods |
|
Consequences |
|
Alternatives
|
GDP implicit price deflator |
|
|
Core inflation rate |
CPI inflation rate exluding volatile elements (food/fuel) |
|
|
|